Who Is at Risk for Developing Macular Degeneration?
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a prevalent eye condition affecting individuals over 50. It leads to the deterioration of the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision.
As it progresses, you may notice blurred or distorted central vision. This makes daily activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces increasingly challenging.
Here's what you need to know to keep your eyesight healthy for years to come.
Key Risk Factors for Developing Macular Degeneration
While some risk factors are beyond control, others can be managed through lifestyle changes and preventive care. Below are ten key contributors to macular degeneration that impact your vision health.
Family History and Genetic Risk
A family history of AMD markedly elevates your risk by up to 70% due to genetic factors. If a parent or sibling has been diagnosed with it, your probability of developing the condition increases significantly. While genetic risk cannot be changed, early detection through regular eye exams can help slow disease progression.
Smoking and Toxin Exposure
Cigarette smoke contains harmful chemicals that reduce oxygen supply to the retina, accelerating cell damage. Even exposure to secondhand smoke increases risk, making smoking cessation one of the most effective ways to protect vision.
Poor Nutrition and Dietary Imbalances
Nutrient deficiencies weaken the macula, increasing the likelihood of vision loss over time. Diets lacking antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and key vitamins contribute to retinal degeneration. Processed foods, excessive sugar, and unhealthy fats promote inflammation in your eyes.
Including a diet rich in antioxidants, particularly lutein and zeaxanthin, supports eye health. Foods such as kale, spinach, broccoli, peas, parsley, and egg yolks are excellent sources of these nutrients.
Cardiovascular Conditions
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and poor circulation negatively impact retinal health. The tiny blood vessels that supply oxygen to the macula become compromised, leading to increased damage. Managing cardiovascular health through diet, exercise, and medication helps maintain proper blood flow to the eyes.
UV and Blue Light Exposure
Long-term exposure to UV rays and high-energy blue light from screens may contribute to retinal damage. The macula is highly sensitive to light-induced stress, which can accelerate degeneration. Protective eyewear and screen filters help minimize exposure and reduce strain on the retina.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle
Excess body weight contributes to chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and circulation problems, all of which impact eye health. Individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) are more likely to experience advanced stages of macular degeneration.
Regular physical activity supports overall circulation and reduces inflammatory responses that harm the retina.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Imbalances
Uncontrolled diabetes damages the small blood vessels in the retina, increasing the risk of macular degeneration. High blood sugar levels trigger oxidative stress, which accelerates retinal cell deterioration. Proper glucose management through diet, exercise, and medication is essential for protecting vision.
Hormonal and Metabolic Changes
Fluctuations in hormones, especially after menopause, may impact retinal function and increase vulnerability to degeneration. Metabolic disorders like insulin resistance can also play a role in disease progression.
Eye Color and Light Sensitivity
Individuals with blue or green eyes have less pigment to filter out harmful light. This reduced natural protection makes them more vulnerable to UV-induced damage. Wearing UV-blocking sunglasses and limiting direct sun exposure can help reduce long-term risks.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy drinking also affects circulation, limiting the retina’s ability to receive necessary oxygen and nutrients. Reducing alcohol consumption supports overall eye health and slows disease progression.
Effective Treatment Approaches for You
While macular degeneration has no cure, several treatment options can help slow its progression and preserve your vision. The right approach depends on whether you have dry (atrophic) or wet (neovascular) macular degeneration.
Dry Macular Degeneration
Dry macular degeneration progresses gradually as retinal cells break down over time. While there is no medical cure, the following strategies can help maintain vision and slow its impact:
- AREDS Supplements: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) recommends a specific formula of vitamins and minerals—vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, copper, and lutein with zeaxanthin—to reduce the risk of progression in intermediate and advanced cases.
- Regular Monitoring: The Amsler grid is a simple at-home tool to detect early visual distortions, helping with early intervention if symptoms worsen.
- Injections: At South Shore Eye Care, LLP, we offer injections to slow Macular Degeneration progression. These injections are for an advanced form of dry AMD called Geographic Atrophy. They target the complement system, a part of the immune system that can contribute to retinal damage in dry AMD.
Wet Macular Degeneration
Wet macular degeneration is more aggressive, caused by abnormal blood vessel growth under the retina. Several medical treatments can slow or prevent further vision loss:
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Medications like Avastin, Lucentis, Eylea, and Vabysmo block vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), preventing new, leaky blood vessels from forming. These injections are typically administered monthly or bi-monthly.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): A light-sensitive drug is injected into the bloodstream and activated with laser treatment to seal off abnormal blood vessels while minimizing retinal damage. This treatment is used in specific cases where anti-VEGF therapy alone is insufficient.
- Laser Therapy: In rare cases, high-energy laser treatment may be used to destroy abnormal blood vessels, though it carries a risk of collateral damage to surrounding retinal tissue.
Vision Support and Rehabilitation
For those with vision loss from macular degeneration, low-vision aids like magnifiers, high-contrast lighting, and screen readers can improve daily tasks. Vision rehabilitation therapy helps you adapt by training them to use their remaining vision effectively.
Simple home modifications, such as enhanced lighting and large-print materials, further improve the safety and accessibility of your environment.
Comprehensive Care at South Shore Eye Care
Our dedicated team of experienced ophthalmologists and optometrists provides personalized care to help manage and slow the progression of retinal conditions. Utilizing the latest technology and evidence-based strategies, we are committed to delivering the highest standard of care. Dr. Raparia, our fellowship trained, board certified ophthalmologist, specializes in the medical management and treatment of retinal diseases, including macular degeneration.
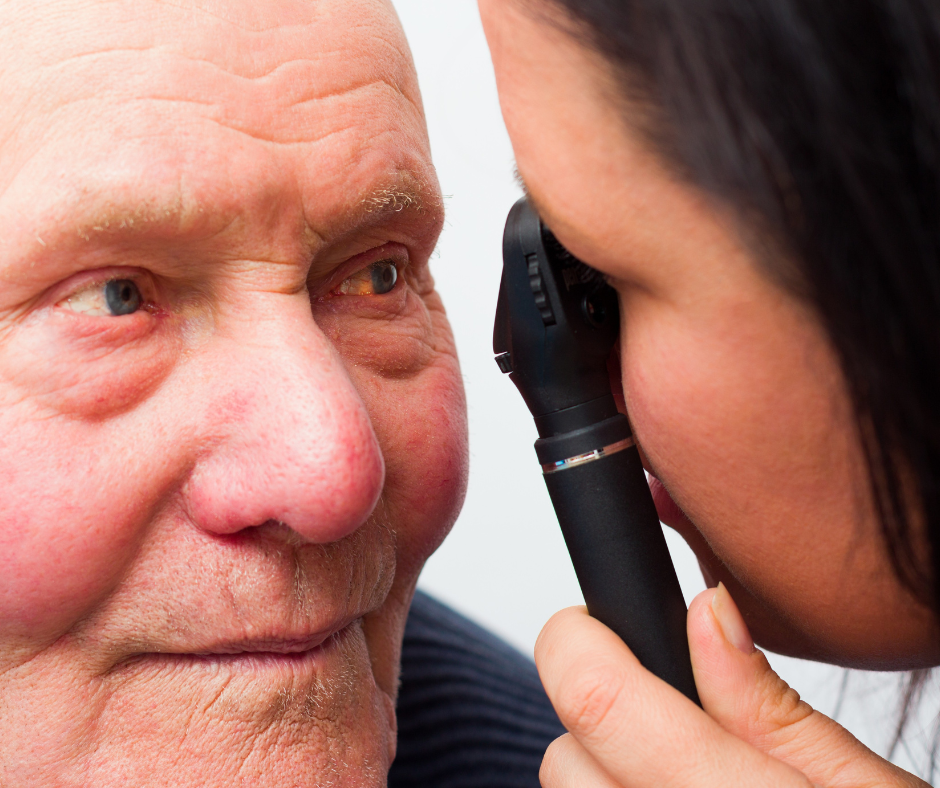
With advanced imaging techniques like optical coherence tomography (OCT) and digital retinal photography, we detect early signs of macular changes before symptoms become severe. Beyond diagnosis and treatment, we prioritize patient education and support, equipping you with the knowledge and resources to protect your vision and maintain independence.
Is your vision fading? Our ophthalmologists and optometrists at
South Shore Eye Care are committed to providing the most advanced care and support to help you maintain your independence and quality of life.
Book an appointment with our experts to take early action to protect your eyesight today!